G-gen 又吉です。今回は、Vertex AI Gemini API の Function Calling を触ってみたの概要を紹介します。

はじめに
Gemini とは
Geminiとは、Google から発表された高性能なマルチモーダルな生成 AI モデルです。テキストおよび画像、動画などの様々な種類のデータを入力、出力として扱えるモデルです。Gemini には、パラメータ規模が異なる Gemini Ultra、Gemini Pro、Gemini Nano の 3 つのモデルがあります。
2023年12月現在、Vertex AI 上では、Gemini Pro が Preview 公開されています。
Function calling とは
Function calling とは、ユーザーの入力(プロンプト)に応じて、事前に定義されたソースコード上の関数から呼ぶべき関数とその関数に渡す引数を Vertex AI Gemini API が JSON で出力してくれる機能のことです。
例えば、「沖縄の天気を教えて?」という入力に対して、通常の LLM では最新の天気予報の情報は持っていないため、正しい情報は帰ってきません。正しい回答を生成するには、地名を引数として最新の天気情報を返す関数を定義しておき、それを呼び出す必要があります。
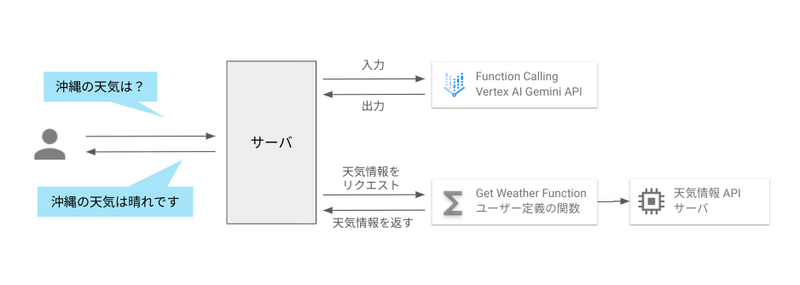
そこで重要となるのが、Function calling です。Function calling を用いると、プロンプトの内容から、Vertex AI Gemini API がどの関数を呼び出すべきかを判断してくれます。その判断を元に、サーバは天気情報を返す関数を実行して、ユーザーへの回答を生成することができます。
事前定義の関数の例として他にも、インターネット検索ができる関数や、EC 上で決済を実行する関数など、様々なユースケースで利用が期待できます。
Function calling の仕組み
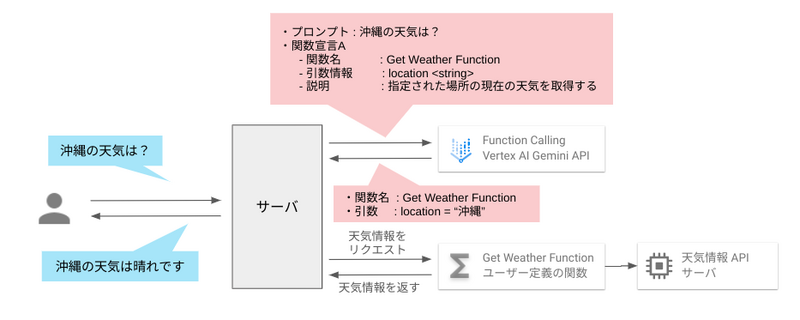
Function calling を利用するには、LLM への入力にプロンプトと合わせて事前定義した関数の情報を記載した関数宣言 (function declarations) を渡す必要があります。 LLM はこの関数宣言から関数の目的を理解し、ユーザーのプロンプトに最適な関数を選択します。
関数宣言には以下の情報を含めます。
- 関数名
- 関数の説明
- 関数パラメーター (引数。OpenAPI スキーマと互換性がある)
# 関数宣言の例 FunctionDeclaration( name="get_current_weather", description="指定された場所の現在の天気を取得する", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "場所" } } }, )
Vertex AI Extensions との違い
Function calling と Vertex AI Extensions は、似た機能ですが、ユースケースによって使い分けることが推奨されています。
例えば、Function calling と Vertex AI Extensions を実行する基盤上に認証情報を含めたくない場合には、 Function calling が適しています。なぜなら、Vertex AI Extensions はそれ自体で関数を実行しますが、Function calling では最適な関数とその引数を応答に含めるだけだからです。
また、数秒以上かかる非同期操作を実行する場合にも、疎結合アーキテクチャの Function calling が適しています。
触ってみる
実行環境
当記事では、Colab Enterprise の Notebook 上で Python を実行します。Colab Enterprise は、マネージドな Notebook のためインフラストラクチャを管理せず実装に注力できます。
Colab Enterprise の Notebook 作成方法は公式ドキュメントのクイックスタートをご参考下さい。
事前準備
Notebook が立ち上がり、ランタイムと接続できましたら以下のコードを実行してライブラリのインストールを行います。
# input:[1]
!pip3 install --upgrade google-cloud-aiplatform
ライブラリのインストールができたら、以下を実行してランタイムを再起動します。
# input:[2] import IPython # ランタイムの再起動 app = IPython.Application.instance() app.kernel.do_shutdown(True)
# output[2] {'status': 'ok', 'restart': True}
次に、Vertex AI インスタンスとモデルの初期化を行います。
# input[3] import requests import vertexai from vertexai.preview.generative_models import ( Content, FunctionDeclaration, GenerativeModel, Part, Tool, ) PROJECT_ID = {プロジェクト ID} LOCATION = "us-central1" # Vertex AI インスタンスの初期化 vertexai.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=LOCATION) # モデルの初期化 model = GenerativeModel("gemini-pro")
今回は、Function Calling の動きを理解するのが目的のため、天気を取得する関数は簡易的な関数として定義します。
# input[4] # 現在の天気を取得するダミー関数 def get_current_weather(location): if location == "東京": return "晴れ" elif location == "沖縄": return "曇り" else: return "雨"
最後に、Function Calling 関数を定義します。
# input[5] # 関数宣言を作成 get_current_weather_func = FunctionDeclaration( name="get_current_weather", description="指定された場所の現在の天気を取得する", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "場所" } } }, ) # LLM が呼び出すツールを定義 weather_tool = Tool( function_declarations=[get_current_weather_func], ) # Function calling 関数を定義 def function_calling(prompt) -> dict: response = model.generate_content( prompt, generation_config={"temperature": 0}, tools=[weather_tool], ) return response
動作確認
まずは、Function callling のレスポンスを確認してみます。
「東京の天気は?」というユーザーのプロンプトに対して、Function calling によって LLM が最適な関数と引数を取得していることがわかります。
尚、レスポンスの出力結果では、日本語の文字列が utf-8 でエンコードされて出力されています。
# input[6] prompt = "東京の天気は?" response = function_calling(prompt) print(response) print("------") if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.name: print(f"最適な関数 : {response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.name}") print(f"必要な引数 : {response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.args.get('location')}") else: print(f"最適な関数 : 何もなし")
# output[6] candidates { content { role: "model" parts { function_call { name: "get_current_weather" args { fields { key: "location" value { string_value: "\346\235\261\344\272\254" } } } } } } finish_reason: STOP safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT probability: NEGLIGIBLE } safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH probability: NEGLIGIBLE } safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT probability: NEGLIGIBLE } safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT probability: NEGLIGIBLE } } usage_metadata { prompt_token_count: 5 total_token_count: 5 } ------ 最適な関数 : get_current_weather 必要な引数 : 東京
続いて、Function calling に与えている関数では解決できないプロンプトを投げてみます。すると、出力には「何もなし」となり想定どおりの挙動です。
# input[7] prompt = "為替レートを教えて?" response = function_calling(prompt) print(response) print("------") if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.name: print(f"最適な関数 : {response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.name}") print(f"必要な引数 : {response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.args.get('location')}") else: print(f"最適な関数 : 何もなし")
# output[7] candidates { content { role: "model" parts { text: "\347\224\263\343\201\227\350\250\263\343\201\202\343\202\212\343\201\276\343\201\233\343\202\223\343\201\214\343\200\201\347\202\272\346\233\277\343\203\254\343\203\274\343\203\210\343\201\253\351\226\242\343\201\231\343\202\213\346\203\205\345\240\261\343\201\257\346\217\220\344\276\233\343\201\247\343\201\215\343\201\276\343\201\233\343\202\223\343\200\202" } } finish_reason: STOP safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT probability: NEGLIGIBLE } safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH probability: NEGLIGIBLE } safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT probability: NEGLIGIBLE } safety_ratings { category: HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT probability: NEGLIGIBLE } } usage_metadata { prompt_token_count: 5 candidates_token_count: 12 total_token_count: 17 } ------ 最適な関数 : 何もなし
最後に、天気を取得するダミー関数の実行までを行います。
# input[8] prompt = "沖縄の天気は?" response = function_calling(prompt) if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call: # 関数名を取得 function_name = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.name # 引数に必要な location を取得 location = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call.args.get("location") # 実行可能な関数 available_functions = { "get_current_weather" : get_current_weather } exec_function = available_functions[function_name] # 関数を実行 function_response = exec_function(location) print(f"「{location}」の天気は、「{function_response}」です。") else: print(f"最適な関数 : 何もなし")
# output[8]
「沖縄」の天気は、「曇り」です。
又吉 佑樹(記事一覧)
クラウドソリューション部
はいさい、沖縄出身のクラウドエンジニア!
セールスからエンジニアへ転身。Google Cloud 全 11 資格保有。Google Cloud Champion Innovator (AI/ML)。Google Cloud Partner Top Engineer 2024。Google Cloud 公式ユーザー会 Jagu'e'r でエバンジェリスト。好きな分野は生成 AI。
Follow @matayuuuu


